Metopic Synostosis (Trigonocephaly) | Symptoms & Causes
What are the symptoms of metopic synostosis?
- A noticeable ridge running down the middle of the forehead
- An overly narrow, triangular shape to the forehead and top of the skull
- Eyes that appear too close together

See our comprehensive guide for patients and families
What causes metopic synostosis?
In most children, metopic synostosis happens without any identifiable reason. Sometimes, however, metopic synostosis occurs as a component of a rare genetic syndrome. The following disorders have been linked to metopic synostosis:
- Baller-Gerold syndrome, which also causes abnormalities in the bones of the arms and hands
- Jacobsen syndrome, which results from missing material within a certain chromosome
- Muenke syndrome, caused by a mutation in the gene that produces a protein responsible for brain and bone tissue health
- Opitz syndrome, which causes several birth defects affecting the face, heart, and larynx
- Say-Meyer syndrome, which is characterized by developmental delays, problems with motor skills. and a short stature
Metopic Synostosis (Trigonocephaly) | Diagnosis & Treatments
How is metopic synostosis diagnosed?
Once an initial finding of metopic synostosis is made, your clinician may take the following steps to confirm the diagnosis:
- Obtaining a full family medical history
- Determining whether your child is experiencing any developmental delays or other problems in meeting age-appropriate milestones
- Measuring the circumference of your child’s head and plotting these measurements on a graph to detect unusual patterns
- Ordering a computed tomography (CT) scan, a non-invasive procedure using X-ray equipment and powerful computers to create detailed images of the skull
After we complete all necessary tests, our experts meet to review and discuss what they have learned about your child’s condition. Then we will talk with you and your family to outline the best treatment options.
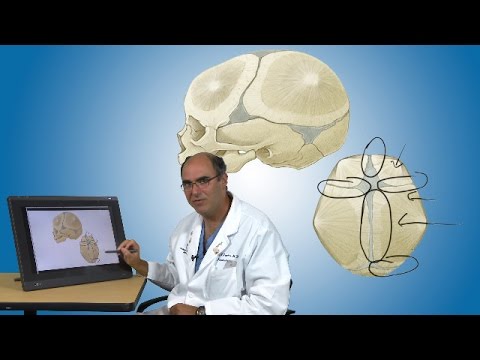
How do we treat metopic synostosis?
Boston Children's Hospital has been a worldwide innovator in diagnosing and treating children with metopic synostosis and all types of craniosynostosis for decades. Clinicians in our Departments of Neurosurgery and Plastic and Oral Surgery have extensive experience in treating all forms and degrees of the condition.
We use minimally invasive techniques — medical and surgical procedures that use small incisions and miniaturized cameras and tools — whenever we can. Boston Children's is a global leader in creating and refining new surgical approaches.
A child with mild metopic synostosis may have no symptoms beyond a noticeable ridge down the middle of his forehead. In these cases, doctors may decide no medical treatment is needed.
Surgery
Many children with moderate to severe metopic synostosis will require surgical intervention.
Surgery for metopic synostosis:
- Is designed to correct deformities in the facial and skull bones
- Often works best in children who are less than 1 year old, since the bones are still soft and pliable, making them easier to manipulate
- May be recommended in much younger infants, including newborns, depending on the severity of their symptoms
- Can also be performed in older children (although the older the child, the more complex the surgery)
- Is usually complete after a single surgery (but in some cases, may need to be repeated over time, depending on the seriousness of the condition)
Before the operation, your child's surgeon will:
- Explain the reasons to consider surgery
- Explain the steps involved in the operation
- Review aftercare instructions, including warning signs of possible complications
During surgery, the surgeon and treatment team will:
- In the case of minimally invasive surgery, use endoscopy — a long, thin tube with an accompanying light and camera — to release the sutures that are abnormally fused
- In the case of reconstructive surgery, reposition the skull bones to allow for normal growth and development
After surgery, your child:
- Will stay in the hospital for one to five days
- May have visible swelling for a few days to a few weeks
- May need to wear a dressing covering her head, protecting the incision site from contamination and infection
- Will need to return for check-ups and evaluations to measure how well the skull, facial bones, and brain are developing
How do we approach metopic synostosis?
Boston Children’s treats hundreds of patients with metopic synostosis and other types of craniosynostosis every year in our Craniofacial Program.
Drawing on our extensive experience treating these disorders in young patients, we will use a multidisciplinary approach to ensure the right treatment for your child's specific symptoms and circumstances.
If, after evaluation, your child is determined to need treatment for his metopic synostosis, members of his Craniofacial Program care team may include:
- Neurosurgeons, who perform surgical procedures on a child’s brain, spinal cord, or nerves
- Plastic surgeons, who diagnose and surgically correct skeletal abnormalities of the skull, facial bones, and soft tissue
- Neurologists, who diagnose, treat, and manage conditions affecting the nervous system
- Oral and maxillofacial surgeons, whose surgical procedures to correct injuries or deformities of the mouth, jaws, face, and skull
- Audiologists, who diagnose, evaluate, and implement treatment approaches for a child’s hearing problems
- Neuroscience nursing professionals, who combine expertise in all aspects of pediatric nursing with a focus on the neurosciences, and act as liaisons between a child’s family and clinical treatment team
- Speech therapists, who evaluate a child’s communicative abilities and formulate treatment plans to enhance and improve speech and language
- Physical therapists, who help children recover, return to their previous level of function, or learn to work within their functional limitations
- Dentists, who maintain a child’s oral health
- Orthodontists, who evaluate the position and alignment of a child’s teeth and help design corrective treatment plans as needed
- Otolaryngologists, or “ear-nose-throat specialists,” who help manage a child’s ear infections, hearing loss, and other related issues that may be tied to a craniofacial abnormality
- Ophthalmologists, who evaluate vision problems and formulate medical or surgical treatment plans to improve or restore vision
- Psychiatrists, who assess a child’s psychosocial functions and behavioral development and can prescribe psychiatric medications if necessary
- Psychologists and social workers, who help children and families express and cope with feelings like worry, fear, frustration, anger, and sadness
Metopic Synostosis (Trigonocephaly) | Coping & Support
In addition to the clinical information offered on this page, Boston Children's has several other resources designed to give your family comfort, support and guidance:
Patient and family resources at Boston Children's
- Boston Children's Behavioral Medicine Clinic helps children who are being treated on an outpatient basis at the hospital — as well as their families — understand and cope with their feelings about:
- Being sick
- Facing uncomfortable procedures
- Handling pain
- Taking medication
- Preparing for surgery
- Changes in friendships and family relationships
- Managing school while dealing with an illness
- Grief and loss
- Boston Children's Psychiatry Consultation Service is comprised of expert and compassionate pediatric psychologists, psychiatrists, social workers, and other mental health professionals who understand the unique circumstances of hospitalized children and their families. The team provides several services, including:
- Short-term therapy for children admitted to one of our inpatient units
- Parent and sibling consultations
- Teaching healthy coping skills for the whole family
- Educating members of the medical treatment team about the relationship between physical illness and psychological distress
- Talking to your child about her condition
- Preparing for surgery and hospitalization
- Supporting siblings
- Taking care of yourself during your child's illness
- Adjusting to life after treatment
- Boston Children's Hale Family Center for Families is dedicated to helping families locate the information and resources they need to better understand their child's particular condition and take part in their care. All patients, families, and health professionals are welcome to use the center's services at no extra cost. The center is open Monday through Friday from 8 a.m. to 7 p.m. and on Saturdays from 9 a.m. to 1 p.m. Please call 617-355-6279 for more information.
- The Boston Children's Hospital Department of Spiritual Care is a source of spiritual support for parents and family members. Our program includes nearly a dozen clergy members — representing Episcopal, Jewish, Lutheran, Muslim, Roman Catholic, Unitarian, and United Church of Christ traditions — who will listen to you, pray with you, and help you observe your own faith practices during your child's treatment.
- Global Services is a dedicated resource for patients and families from countries outside the United States. The center can provide assistance with everything from reviewing medical records to setting up appointments and locating lodging. Contact the center by phone at +1-617-355-5209 or via e-mail at international.center@childrens.harvard.edu.
Helpful links
Please note that neither Boston Children's Hospital nor the Craniofacial Anomalies Program at Boston Children's unreservedly endorses all of the information found at the sites listed below. These links are provided as a resource.
- AboutFace International
- Changing Faces
- Children's Craniofacial Association
- Facebook Group: Craniosynostosis Support for Parents and Guardians
- FACES: The National Craniofacial Association
- Foundation for Faces of Children
- Headlines: The Craniofacial Support Group
- International Craniofacial Institute
- World Craniofacial Foundation
Metopic Synostosis (Trigonocephaly) | Research & Clinical Trials
Among our research efforts with promise for treating metopic synostosis and other types of craniosynostosis are:
- Mark Proctor, MD, Boston Children’s neurosurgeon, has authored several key papers about endoscopic approaches to the treatment of craniosynostosis. In addition, he was the lead neurosurgeon involved in developing formal parameters of care for the condition.
- John Meara, MD, DMD, MBA, Boston Children's plastic surgeon-in-chief, is analyzing the genetic, phenotypic, cognitive, and behavioral aspects of craniosynostosis.
- Bonnie Padwa, MD, PhD, Boston Children's oral surgeon-in-chief, is assessing facial growth patterns in children with several craniofacial anomaly types.
Clinical trials
Boston Children’s is known for pioneering some of the most effective diagnostic tools, therapies and preventive approaches in pediatric medicine. A significant part of our success comes from our commitment to research — and to advancing the frontiers of mental health care.
Boston Children’s coordinates hundreds of clinical trials at any given time. Clinical trials are studies that may involve:
- Evaluating the effectiveness of a new drug therapy
- Testing a new diagnostic procedure or device
- Examining a new treatment method for a particular condition
- Taking a closer look at the causes and progression of specific diseases
While children must meet strict criteria in order to be eligible for a clinical trial, your child may be eligible to take part in a study. Before considering this option, you should be sure to:
- Consult with your child’s treating physician and treatment team
- Gather as much information as possible about the specific course of action outlined in the trial
- Do your own research about the latest breakthroughs relating to your child’s condition
If your physician recommends that your child participate in a clinical trial, you can feel confident that the plan detailed for that study represents the best and most innovative care available. Taking part in a clinical trial at Boston Children’s is entirely voluntary. Our team will be sure to fully address any questions you may have, and you may remove your child from the medical study at any time.


